BabyAGI
BabyAGI was one of the first multi-agent systems that used LLMs for performing useful tasks. It makes use of several different types of agents, such as a task creation agent and an execution agent, as shown in the diagram below.
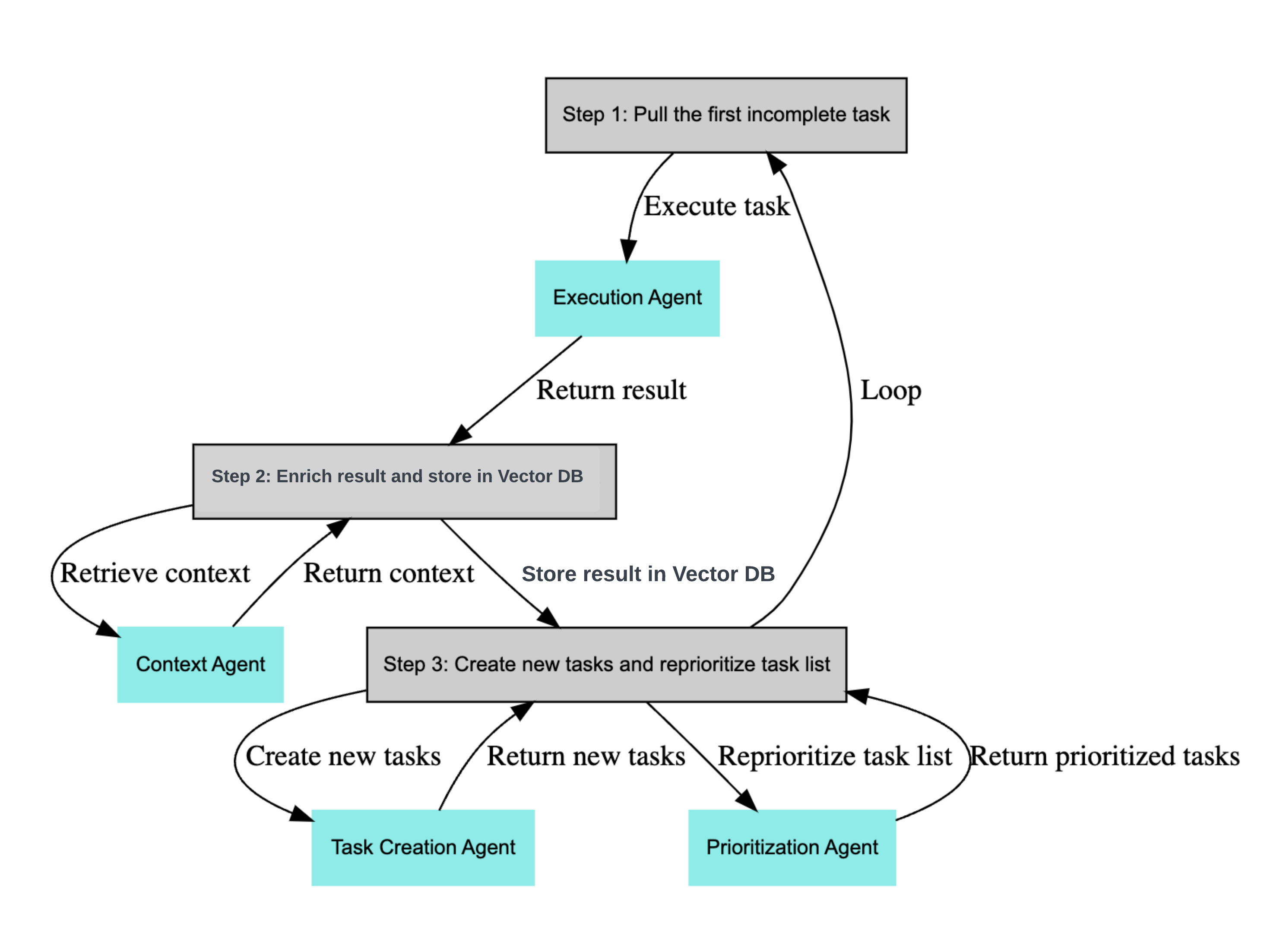
However, here's Yohei (creator of BabyAGI) admitting that BabyAGI isn't a true multi-agent system since the agents use the same LLM and code base, and run on the same server.
Using the Naptha SDK and node infrastructure, we implemented BabyAGI as a true multi-agent system for the first time. You can check out a demo video of this multi-node workflow here.
Prerequisities
Make sure you have the Naptha SDK installed.
Modules Used
The BabyAGI multi-node workflow is made up of the following components, which you can find on the Naptha GitHub:
| Module | Description | Repository |
|---|---|---|
| Orchestrator Flow | Multi-agent task solving across a network of multiple nodes. | GitHub |
| Task Initiator | BabyAGI task initiator agent. | GitHub |
| Task Executor | BabyAGI task executor agent. | GitHub |
| Task Finalizer | BabyAGI task finalizer agent. | GitHub |
Run
You can run the BabyAGI flow from the SDK using the following command:
naptha run orchestrator:babyagi -p "objective='Research the history of football'" --agent_nodes "node.naptha.ai,node1.naptha.ai"
Configuration Breakdown:
objective: Your desired research or task objectiveagent_nodes: Comma-separated list of agent node URLs
This runs the flow across three nodes in total - one orchestrator node (whichever you have set as the NODE_URL in the .env file of the Naptha SDK), and two agent nodes (that you have set using the --agent_nodes flag).
Start with simple objectives to understand the workflow, then gradually increase complexity as you become familiar with the system.